Variational perturbation theory
In mathematics, variational perturbation theory (VPT) is a mathematical method to convert divergent power series in a small expansion parameter, say
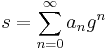 ,
,
into a convergent series in powers
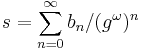 ,
,
where 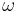 is a critical exponent (the so-called index of "approach to scaling" introduced by Franz Wegner). This is possible with the help of variational parameters, which are determined by optimization order by order in
is a critical exponent (the so-called index of "approach to scaling" introduced by Franz Wegner). This is possible with the help of variational parameters, which are determined by optimization order by order in 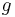 . The partial sums are converted to convergent partial sums by a method developed in 1992[1].
. The partial sums are converted to convergent partial sums by a method developed in 1992[1].
Most perturbation expansions in quantum mechanics are divergent for any small coupling strength $g$. They can be made convergent by VPT (for details see the first textbook cited below). The convergence is exponentially fast[2] [3].
After its success in quantum mechanics, VPT has been developed further to become an important mathematical tool in quantum field theory with its anomalous dimensions[4]. Applications focus on the theory of critical phenomena. It has led to the most accurate predictions of critical exponents. More details can be read here.
References
- ^ Kleinert, H. (1995). "Systematic Corrections to Variational Calculation of Effective Classical Potential". Phys. Lett. A 173: 332. http://users.physik.fu-berlin.de/~kleinert/213/213.pdf.
- ^ Kleinert H. and Janke W. (1993). "Convergence Behavior of Variatioal Perturbation Expansion - A Method for Locating Bender-Wu Singularities". Phys. Lett. A 206: 283. http://users.physik.fu-berlin.de/~kleinert/235/235.pdf.
- ^ Guida R., Konishi K., and Suzuki H. (1996). "Systematic Corrections to Variational Calculation of Effective Classical Potential". Ann. Phys. (N.Y.) 249: 109. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WB1-45V7F53-22-1&_cdi=6697&_user=1676895&_pii=S0003491696900664&_origin=search&_coverDate=07%2F10%2F1996&_sk=997509998&view=c&wchp=dGLbVtz-zSkzk&md5=161cd093bb98727f8731cd5c96190848&ie=/sdarticle.pdf.
- ^ Kleinert H. (1998). "Strong-coupling behavior of φ^4 theories and critical exponents". Phys. Rev. D 57: 2264. Bibcode 1998PhRvD..57.2264K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.57.2264. http://users.physik.fu-berlin.de/~kleinert/257/257.pdf.
References
- Kleinert H., Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics, Statistics, Polymer Physics, and Financial Markets, 3. Auflage, World Scientific (Singapore, 2004) (readable online here) (see Chapter 15)
- Kleinert H. and Verena Schulte-Frohlinde, Critical Properties of φ4-Theories, World Scientific (Singapur, 2001); Paperback ISBN 981-02-4658-7 (readable online here) (see Chapter 19)
- Feynman, Richard P.; Kleinert, Hagen (1986), "Effective classical partition functions", Phys. Rev., A 34 (6): 5080–5084, December 1986, Bibcode 1986PhRvA..34.5080F, doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.34.5080, PMID 9897894